TIL: R-strings Are Essential for Regex Pattern Matching with RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
- November 29, 2024
Today I learned the importance of r-strings (raw strings) when using regex patterns with LangChain’s RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter. I was working on a project to split a book into chapters for knowledge graph ingestion, and what seemed like a simple regex pattern wasn’t working as expected.
The Task
I needed to split a book’s text content into chapters based on chapter headings to provide an example of a Hierarchical Lexical Graph for an upcoming course.
I had flattened the book into a single string, and then needed to split the text on patterns like "CHAPTER {number}" along with other section markers like “Index”, “Preface”, and “Table of Contents”. Seemed straightforward enough!
The Problem
My initial code looked something like this:
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
separators=[
"\nCHAPTER\s+\d", # This didn't work!
"\nIndex\n",
"\nPreface\n",
"\nTable of Contents\n",
],
is_separator_regex=True
)Despite the pattern looking correct, it wasn’t matching the chapter headings. After a couple of hours of debugging, and a lot of help from Michael Hunger, we Michael found the solution.
The issue was with how Python interprets backslashes in regular strings.
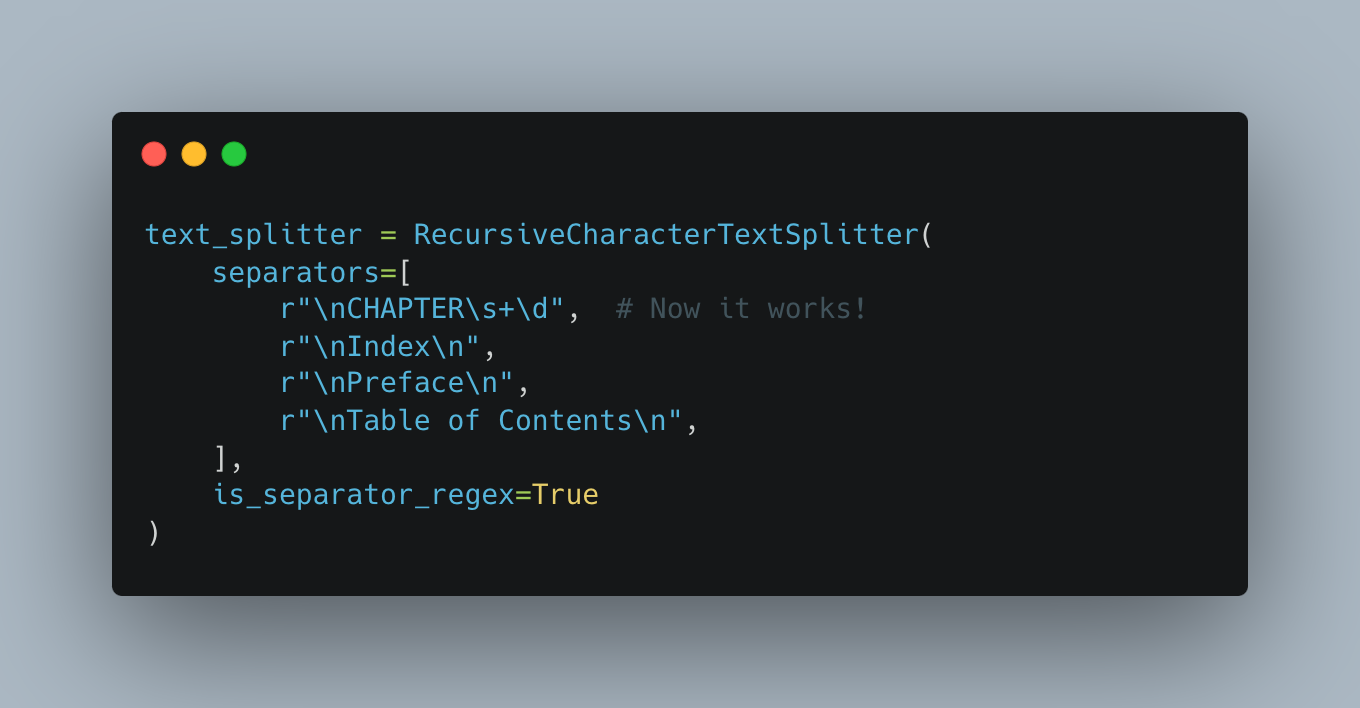
The solution? Use r-strings (raw strings) for the regex patterns
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
separators=[
r"\nCHAPTER\s+\d", # Now it works!
r"\nIndex\n",
r"\nPreface\n",
r"\nTable of Contents\n",
],
is_separator_regex=True
)Why It Works
In Python, the r prefix creates a raw string where backslashes are treated literally. Without it, Python interprets \n as a newline character and \s as an escaped ‘s’, breaking the regex pattern. With r-strings, \n and \s are preserved as-is, allowing the regex engine to interpret them correctly.
Key Takeaway
When working with regex patterns in Python, especially in text processing libraries like LangChain, always use r-strings (r"pattern") to ensure backslashes are interpreted correctly. It’s a small detail that can save hours of debugging!
head to Neo4j GraphAcademy and enrol now.